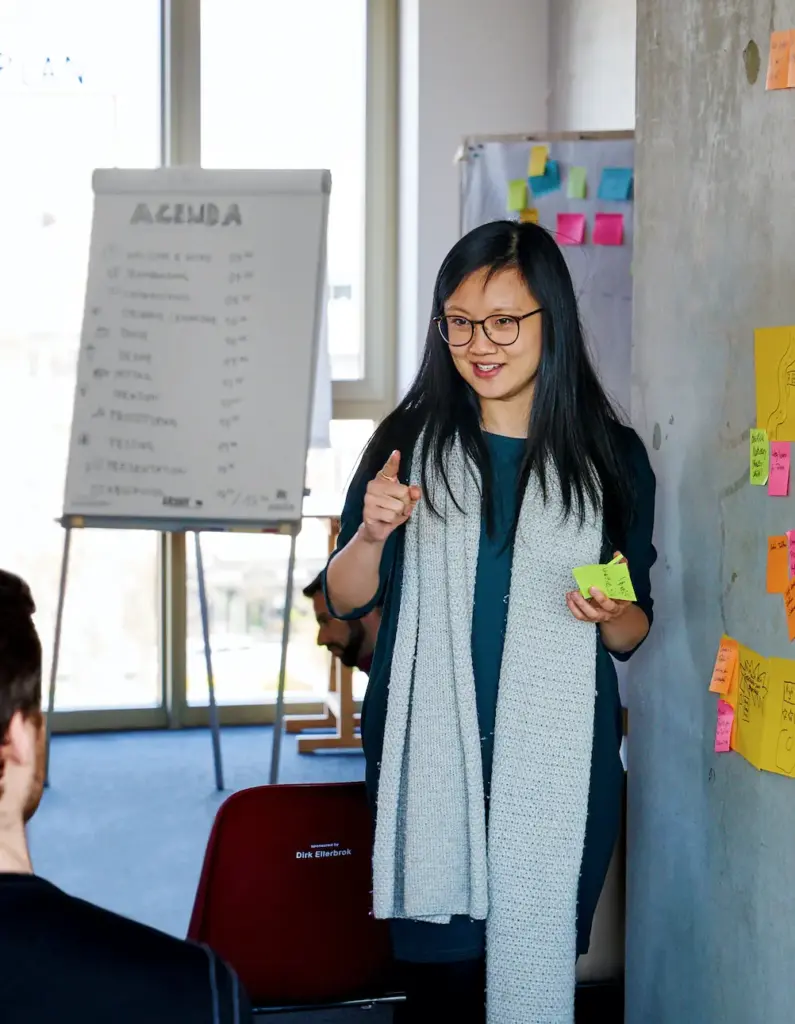
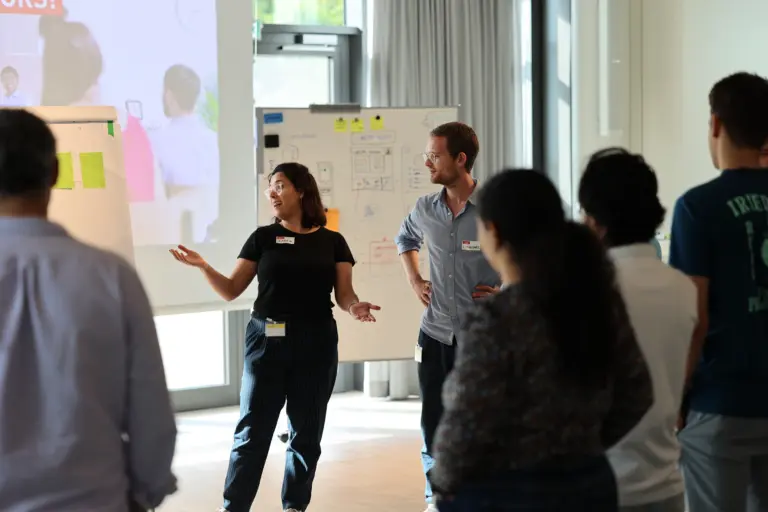
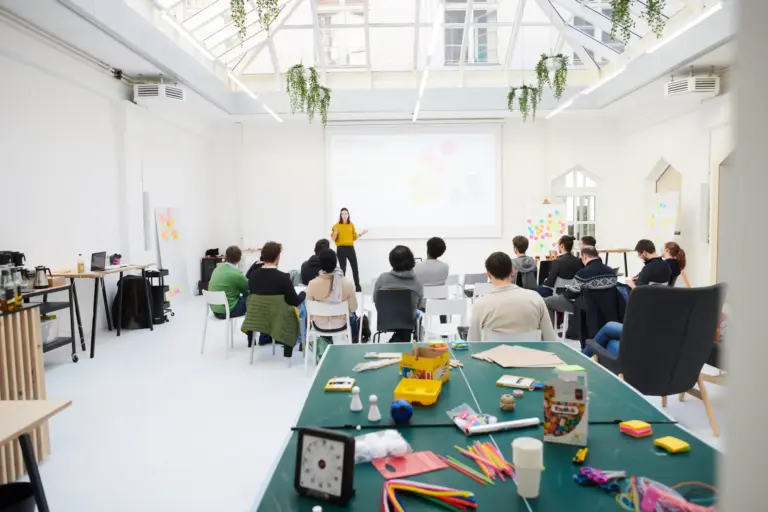
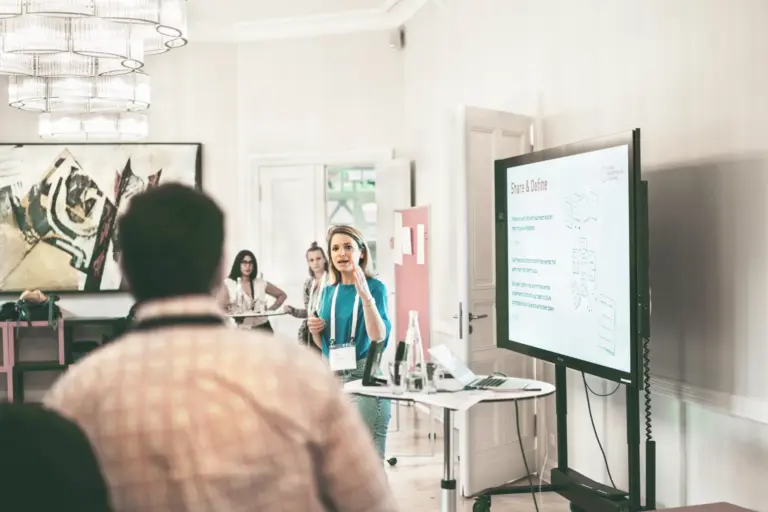
Design thinking is an iterative process that combines creativity, critical thinking, and structured analysis to develop innovative solutions. Each phase of the process aims to better understand the needs of user groups or to adapt and improve ideas. Repeatedly going through the various phases results in tailor-made, user-centered outcomes.
It all starts with a challenge. This involves outlining in one sentence what experience needs to be improved. For example: Design a way to make team decisions more effectively.
The team then goes through the design thinking phases. First linearly, then iteratively.
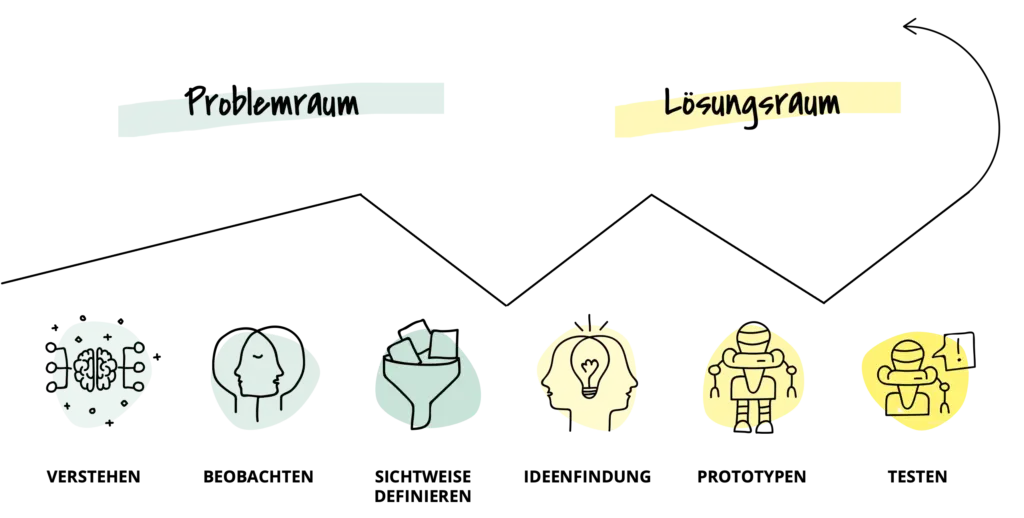
Understand: The goal is to develop a common understanding of the challenge. Using methods such as mind maps or stakeholder maps, team members bring themselves to the same level of knowledge and develop an understanding of potential user groups and their needs. This phase is fundamental to effective, non-hierarchical collaboration and prepares the team for the following steps.
Empathy: Here, participants learn to put themselves in the shoes of user groups. This is done through direct observation, role-playing, and, in particular, interviews with users. Specially developed interview techniques and plans help to gain in-depth insights into the needs and motivations of users.
Synthesis: Based on the interviews, each team creates a focused “point of view” (POV). Through storytelling and joint analysis, needs are identified and summarized in a user-centered problem statement. This POV helps to find focus and summarize it in a tangible way for further work.
Finding ideas: In this phase, the team generates a variety of ideas. Based on the POV, creative “How could we…” questions are formulated. Brainstorming techniques foster a creative atmosphere in which unconventional ideas are valued.
Building prototypes: The team selects a solution from the ideas developed and implements it in an initial prototype. Various prototyping methods such as role-playing, paper mockups, or Lego models make the ideas tangible. The goal is to concretize the idea so that it can be effectively evaluated with users in the test phase.
Testing: The prototypes are tested with users to gather valuable feedback. An authentic test environment makes it possible to obtain honest feedback. This feedback is essential for the subsequent iteration and further development of the ideas.